Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Malins, A.; Lemoine, T.*
Journal of Open Source Software (Internet), 7(71), p.3318_1 - 3318_6, 2022/03
Suyama, Kenya; Yokoyama, Kenji
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (119), p.38 - 47, 2018/02
We have developed numerous neutronics calculation codes in Japan. However, development of the one-point burnup calculation code which replaces the still widely used ORIGEN2 code has not been successful. The one point burnup code is indispensable to evaluate the characteristics of the used nuclear fuel increasing in Japan, and it uses all evaluated nuclear data including the fission yield and decay data as well as cross section data. It means that it could be the Killer Application in the field of the nuclear data and neutronics code. This report describes the necessity of the one point burnup calculation code development in Japan and required function and performance which have been considered by authors.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.12025_1 - 12025_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:90.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recently, intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerator have been proposed for various applications. Accurate and comprehensive deuteron nuclear data library over wide ranges of target mass number and incident energy are indispensable for the design of deuteron accelerator neutron sources. Thus, we have developed an integrated code system dedicated for analysis and prediction of deuteron-induced reactions, which is called DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS). In the present work, the analysis of  reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to
reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to 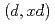 reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the
reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the  and
and 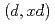 reactions well.
reactions well.
 reactions on
reactions on  Be and
Be and  C at incident energies up to 50 MeV
C at incident energies up to 50 MeVNakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
Physical Review C, 94(1), p.014618_1 - 014618_9, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:90.01(Physics, Nuclear)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) from deuteron bombardment on thick Be and C targets are analyzed using the DEURACS (DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System). The calculated TTNYs reproduced the experimental ones quantitatively well in the incident energy range up to 50 MeV. In addition, it was found that the proton stripping reaction makes the most dominant contribution to neutron production. From the analysis, we conclude that the DEURACS is applicable to  reactions and modeling of the stripping reaction is essential to predict neutron production yields accurately.
reactions and modeling of the stripping reaction is essential to predict neutron production yields accurately.
Suyama, Kenya; Hirao, Yoshihiro*; Sakamoto, Hiroki*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 57(12), p.787 - 791, 2015/12
, 57(12), p.787 - 791, 2015/12
In the measures to pursue the world's highest level of safety of the nuclear installations, it is required to maintain the technical revel of the safety analyses codes as higher as possible. Because many of them were introduced from US at the initial phase of the nuclear energy introduction, development of computer codes and relevant tools in Japan have not been continued successfully. Accordingly, many old US-oriented code has been used. This manuscript presents the current status and the problems of computer codes for nuclear safety evaluation, and a scheme to introduce the computer codes of Japan, which in-cooperate the latest knowledge, in the scene of nuclear safety regulation and practical purpose.
Sato, Tatsuhiko
Hoshasen, 31(4), p.313 - 318, 2005/10
Evaluation of high-energy neutron dose is one of the key issues in the shielding design of accelerator facilities and in the planning of long-term space missions. High-energy neutron transport simulation codes play an important role in the evaluation, since there is a large difficulty in the precise measurement of high-energy neutron doses. This paper reviews the Monte-Carlo simulation codes applicable to the purpose, and summarizes the requirements for the future development of the codes.
Information Systems Operating Division
JAERI-Review 2005-032, 151 Pages, 2005/08
Center for Promotion of Computational Science and Engineering (CCSE) of Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) installed large computer systems including super-computers in order to support research and development activities in JAERI. CCSE operates and manages the computer system and network system. This report presents usage records of the JAERI computer system and the big users' research and development activities by using the computer system in FY2004 (April 1, 2004 - March 31, 2005).
Center for Promotion of Computational Science and Engineering
JAERI-Review 2005-008, 199 Pages, 2005/03
The Center for Promotion of Computational Science and Engineering (CCSE) in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) installed large computer system including super-computers in order to support research and development activities in JAERI. CCSE is also operate anad manage the computer system and network system. This report presents the survey results of research and development activities by using JAERI computer system in FY2003.
Nuclear Code Evaluation Special Committee of Nuclear Code Research Committee
JAERI-Tech 2003-078, 107 Pages, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Tomoyuki*; Amano, Hikaru; Uchida, Shigeo*; Ikeda, Hiroshi*; Matsuoka, Shungo*; Hayashi, Hiroko*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*
Kankyo Eisei Kogaku Kenkyu, 17(3), p.340 - 344, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Nomura, Yasushi; Takada, Tomoyuki; Kadotani, Hiroyuki*; Kuroishi, Takeshi
JAERI-Tech 2003-020, 88 Pages, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Iijima, Susumu; Okajima, Shigeaki
JAERI-Data/Code 2002-023, 44 Pages, 2002/12
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Takuya; Togawa, Orihiko
Proceedings from the International Conference on Radioactivity in the Environment (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2002/09
A marine environmental assessment system STEAMER is developing for predicting the short-term (30days) dispersion and assessing the collective dose to the Japanese population due to radionuclides released to the ocean. The computer code system for short-term predictions of radionuclide dispersion is a combination of the Princeton Ocean Model (POM) for predicting ocean currents and a particle random walk model SEA-GEARN for oceanic dispersion of dissolved radionuclides. The system has been applied to a hypothetical accident of a nuclear submarine if it sinks in an offshore region around Japan, by using measured currents, temperature, salinity and meteorological regional objective analysis data (RANAL). Another computer code system DSOCEAN is also applied to the same hypothetical accident in order to compare the results of radionuclide dispersion in the ocean and the collective dose to the Japanese population. An equidistant-grid compartment model combined with a model of the geostrophic current analysis is used in DSOCEAN.
*;
JNC TN8400 2001-027, 131 Pages, 2001/11
In order to document a basic manual about input data, output data, execution of computer code on groundwater flow and radionuclide transport calculation in heterogeneous porous rock, we investigated the theoretical background about geostastical computer codes and the user's manual for the computer code on groundwater flow and radionuclide transport which calculates water flow in three dimension, the path of moving radionuclide, and one dimensional radionuclide migration. In this report, based on above investigation we describe the geostastical background about simulating heterogeneous permeability field. And we describe construction of files, input and output data, a example of calculating of the programs which simulates heterogeneous permeability field, and calculates groundwater flow and radionuclide transport. Therefore, we can document a manual by investigating the theoretical background about geostastical computer codes and the user's manual for the computer code on groundwater flow and radionuclide transport calculation. And we can model heterogeneous porous rock and analyze groundwater flow and radionuclide transport by utilizing the information from this report.
Nakakawa, Masayuki
Robutsuri No Kenkyu, (51), p.47 - 51, 2000/12
no abstracts in English
Nakahara, Yoshinori; Suyama, Kenya; Suzaki, Takenori
JAERI-Tech 2000-071, 381 Pages, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Sakurai, Kiyoshi; Kume, Etsuo; Yatabe, Shigeru*; Maekawa, Fujio; Yamamoto, Toshihiro; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Mori, Takamasa; Ueki, Kotaro*; Naito, Yoshitaka*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 42(10), p.1062 - 1065, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Ohtaki, Akira; ; ; *; *;
JNC TN9410 2000-006, 74 Pages, 2000/04
To evaluate materials balance in nuclear fuel cycle quickly and quantitatively the fuel cycle requirement code "FAMILY" was improved. And an accumulated TRU&LLFP quantity analysis code was developed. The contents are as follows: (1)A calculation ability of minor actinide production and expenditure was added to the "FAMILY" code. (2)An output program for the "FAMILY" calculation results was developed. (3)A simple version of "FAMILY" code was developed. (4)An analysis code for accumulated TRU&LLFP quantity in nuclear fuel cycle was developed.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; *; Okano, Yasushi; *; Yamaguchi, Akira
JNC TY9400 2000-012, 91 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
; Sato, Wakaei*;
JNC TN9400 2000-037, 87 Pages, 2000/03
ln order to compare the nuclear characteristics of water-cooled bleeder cores with that of LMFBR, MOX fuel cell models are established for boiling and non-boiling LWR, non-boiling HWR and sodium-cooled reactor. Frst, the comarison is made between the heterogeneous cell calculation results by SRAC and those by SLAROM. The results show some differences as for neutron energy spectrum, one-grouped cross section and conversion ratio due to the different grouped cross section library (both are based on JENDL-3.2, though) used for each code, however, the difference is acceptably small for grasping the basic characteristics of the above-mentioned cores. Second, using the SLAROM code, main core parameters such as mean neutron energy, ratio of fast neutron and  -value, are analyzed. The comparison between the cores show that softened neutron spectrum by the scattering effect of hydrogen or heavy hydrogen increase the contribution of nuclear reaction (especially for neutron capture reaction rather than fission reaction) in lower energy region comparing with LMFBR. ln order to overcome the effect, tighter lattice than LMFBR is necessary for water-cooled cores to realize the breeding of fissile nuclides. Third, effects of Pu isotopic composition on the breeding ratio are evaluated using SRAC burnup calculation. From the results, it is confirmed that degraded Pu (larger ratio of Pu-240) show the larger breeding ratio. At last, sensitivity analyses are made for k-effective and main reaction ratios. As for k-effective, using a temporary covariance data of JENDL-3.2, uncertainty resulting from the cross sections' error is analyzed for a boiling LWR and a sodium-cooled reactor. The boiling LWR core shows larger sensitivity in lower energy region than the sodium-cooled reactor (especially for the energy region lower than 1kev), And, 18-group analysis that is considered acceptably good for LMFBR analysis, should not be enough for accurate sensitivity estimation of ...
-value, are analyzed. The comparison between the cores show that softened neutron spectrum by the scattering effect of hydrogen or heavy hydrogen increase the contribution of nuclear reaction (especially for neutron capture reaction rather than fission reaction) in lower energy region comparing with LMFBR. ln order to overcome the effect, tighter lattice than LMFBR is necessary for water-cooled cores to realize the breeding of fissile nuclides. Third, effects of Pu isotopic composition on the breeding ratio are evaluated using SRAC burnup calculation. From the results, it is confirmed that degraded Pu (larger ratio of Pu-240) show the larger breeding ratio. At last, sensitivity analyses are made for k-effective and main reaction ratios. As for k-effective, using a temporary covariance data of JENDL-3.2, uncertainty resulting from the cross sections' error is analyzed for a boiling LWR and a sodium-cooled reactor. The boiling LWR core shows larger sensitivity in lower energy region than the sodium-cooled reactor (especially for the energy region lower than 1kev), And, 18-group analysis that is considered acceptably good for LMFBR analysis, should not be enough for accurate sensitivity estimation of ...